Could deflation wreak havoc in the housing market?
03-25-2015
If deflation goes on for a fraction too long it could unravel UK house prices

There's a fine line between good and bad deflation when it comes to the UK's sentiment-driven housing market.
Increase your business' digital presence
A new government programme includes £2m of funding to help small businesses boost their digital audience
By Anna White, Property correspondent
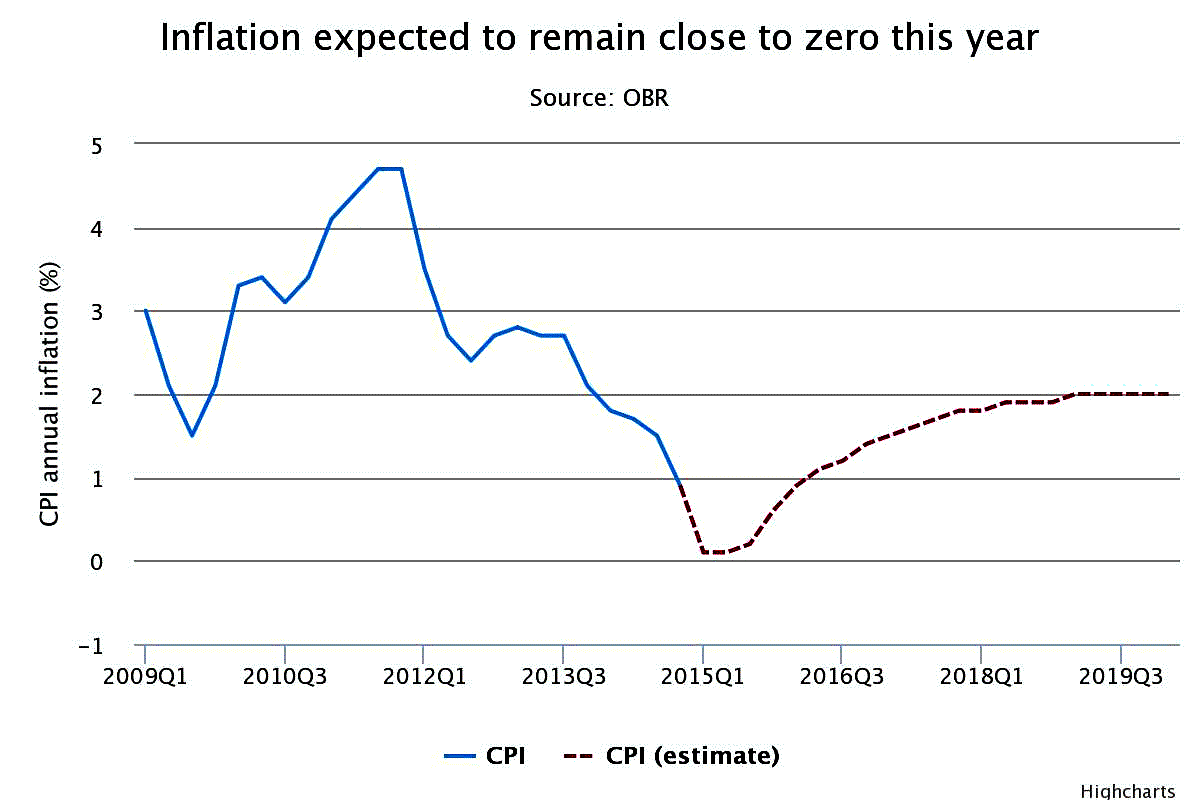
Inflation hit zero for the first time on record in February, sparking concerns that long-term deflation could wreak havoc in a muted UK housing market already spooked by general election uncertainty.
New data from the Office of National Statistics showed that inflation fell 0.3pc on January, measured by the Consumer Price Index CPI), as the cost of food, toys, games and books got cheaper.
In the short term, cheaper consumer products act as an extra boost to house prices, which have been going up while the cost of material goods has been going down.
However, if deflation goes on for a fraction too long it could flip a switch in the housing market.
Good deflation
Deflation is categorised into two types “good deflation” and “bad deflation” - but in housing market terms there is a fine line between the two.
Good forms of deflation are generally created by bountiful, growing supply, and a sign that the wheels of industry are turning.
The recent over-supply of oil has led to falling prices at the pumps, and reduced the cost of the production and transport of material goods, contributing to disinflation in the UK.
READ: Opec is willing to wait out the oil price slump
READ: Aldi to open more stores than Tesco, Sainsburys and Morrisons combined
It has also enabled intense competition among the supermarkets as they reduce food prices to ward off the attack from discount grocers, Aldi and Lidl.
The end result? Your shopping basket is cheaper.
Lower day-to-day prices puts more money in the householder’s pocket, meaning they are more likely to consider a move to get that extra bedroom or 50sq ft of garden.
With interest rates also low credit becomes cheaper, leading to more activity in the mortgage market.
“More pounds in the pocket means there is more ability to withstand mortgage payments,” said Jan Crosby, head of real estate at KPMG. “In turn this will drive transactions and confidence,” and therefore give house prices a boost.
For Adam Challis, head of residential research at JLL, “good” and “bad” deflation is another way of saying short and long term.
“Good deflation means there is no expectation that things are going to keep getting cheaper. People just spend now, money will swill around for a bit and have a positive impact on the housing market.”
However, if people think deflation is here tomorrow they will under invest today, he said.
At this point good deflation can turn sour.
Bad deflation
Bad deflation - as seen in Japan over the last two decades and now a lurking threat in the eurozone - is down to subdued inflationary pressures.
People stop buying goods as they predict prices will be cheaper in a few months, sending products into a value spiral hitting business turnover and therefore, eventually, jobs.
According to Anthony Codling, an analyst at the broker, Jefferies, this is dire news for existing homeowners.
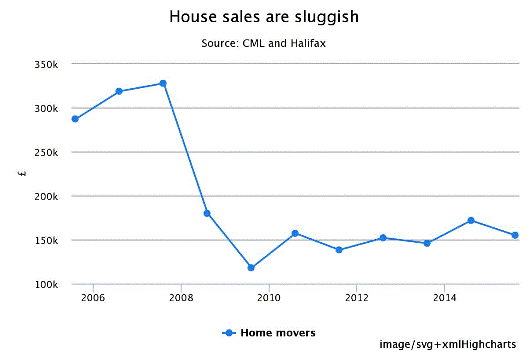
New data from the ONS has shown that UK house prices fell 0.2pc between December and January. Even more telling, the annual rate of house price growth slipped from 9.8pc to December to 8.4pc for the 12 months to January - and any slight drop in house prices makes it harder for people to move.
“If property prices drop existing homeowners will struggle to trade up, as a lower selling price will force them to take on a higher loan-to-value mortgage,” said Mr Codling. This will slow transactions, hitting house prices as demand to move cools further.
A subtle shift in the homeowner’s mindset about deflation - for example people worrying about their job prospects or potential reductions in pay packet - will also inhibit the potential mover, quashing sales volumes which, according to Mr Codling, is one of the lead indicators for falling house prices along, with credit availability.
There is a similarity here between consumer and homeowner behaviour, he said.
In a bad deflationary environment people delay buying a new TV because they think it will be cheaper in six months. The same applies to the housing market.
“Why would you buy if you think prices are going to go lower? Homeowners like buying into a rising market,” he said.
Bad deflation is indicative of a weakening economy which will also spook a housing market so sensitive to interest rate noise or political events such as the general election.
“Sustained and persistent deflation is a worry,” said Mr Crosby. “But we are months from that.”
Winners and losers
Theoretically, first-time buyers should benefit from falling house prices making expensive areas such as London and the South East more affordable.
However, longer term deflation could threaten the income of first and second jobbers, those last through the door in the workplace, preventing young workers, couples and families getting on the property ladder.
The one beneficiary in a longer term, deflationary scenario could be the cash-rich, buy-to-let investor, able to pick up cheap property.
With pension reform coming into effect in April, the over-55s, who will be able to withdraw their pension in one lump sum, may well choose to sink it into property, again reducing the choice for first-time buyers.
“I think we are comfortable that deflation is temporary and not expected to be an embedded part of the UK economic story,” said Mr Challis.
This is welcome news to the housing market, which has already been stalled by the upcoming general election.
“People are more focused on politics and pre-election rhetoric rather than deflation,” said Mr Challis.
And if Britain looks as if it will fall into longer term or bad deflation, the governor of the Bank of England has the tools to reverse it, by lowering interest rates even further.
Which is of course, another story for the housing market.


